


Once considered simple lifting tools, jib cranes are now equipped with automation technologies that significantly boost performance, safety, and operational efficiency. Whether you are using a freestanding jib crane, wall mounted jib crane, or articulating jib crane, integrating automation is no longer optional—it's essential.
In this comprehensive guide, we explore how automation enhances jib crane functionality, what smart features are available, and how different crane types adapt to automated environments.
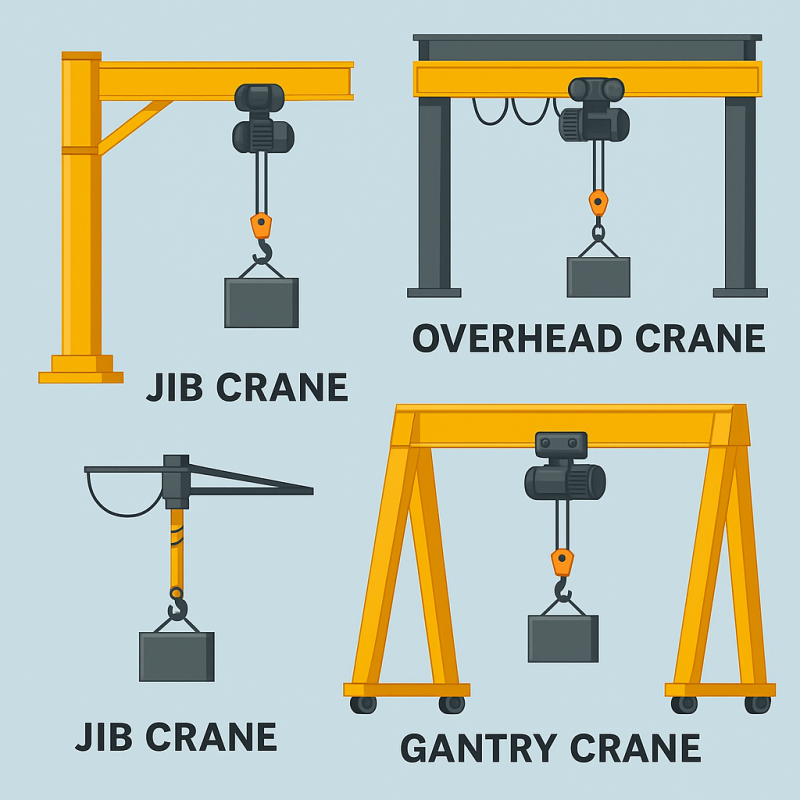
Before diving into automation, it’s important to understand the foundation of these machines. Jib cranes are material handling devices with a horizontal boom (the jib) that supports a moveable hoist. They offer radial movement around a fixed point and are commonly used in manufacturing, construction, and warehousing.
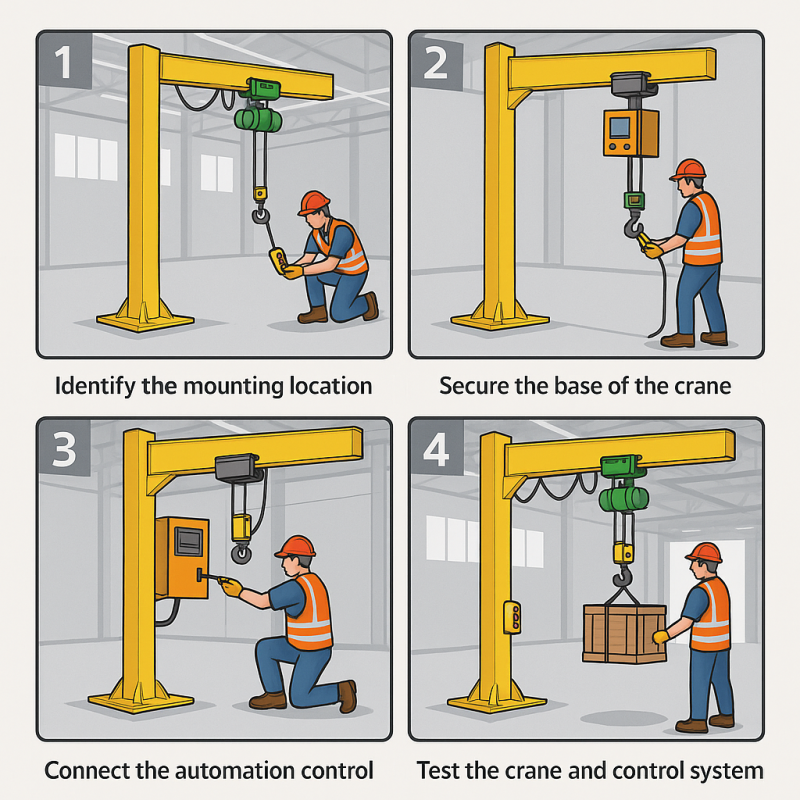
If you’re new to the concept, start with this overview of how to install jib cranes.
There are multiple types of jib cranes, each with unique installation requirements and motion capabilities. According to the detailed jib crane specification, the most common variants include:
Freestanding Jib Crane: Installed on reinforced floors, offering 360° rotation.
Wall Mounted Jib Crane: Mounted on building walls, ideal for narrow workspaces.
Ceiling Mounted Jib Crane: Suspended from overhead structures for floor-free operation.
Articulating Jib Crane: Provides flexible motion via double arms, excellent in cluttered environments.
Pillar Jib Crane: Ideal for repetitive light-duty lifting near a workstation.
To compare with other systems, explore cranes and jib cranes solutions.

Automation allows cranes to go beyond manual lifting by integrating technologies such as:
Motorized slewing and trolley movement
Programmable lift and drop positions
Sensors for overload and alignment detection
IoT-based data logging
Remote or touch-screen controls
These technologies help minimize human error, improve precision, and reduce downtime.
One of the biggest advantages of automation is safety enhancement. Smart sensors prevent overloads, detect obstructions, and even shut down operations if unsafe conditions are detected.
Load Sensors: Monitor weight to prevent mechanical failure.
Collision Avoidance: Stops movement when a person or object enters a danger zone.
Speed Control: Automates hoist speed for stable load handling.
These features make a significant difference in high-risk industrial settings.
Automated jib cranes can memorize and repeat motion paths, improving productivity in repetitive tasks. Some models support auto-return functionality, further saving time in assembly and material transfer operations.
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC) allow pre-configured lifting paths.
Multi-axis motion (especially in articulating models) enables complex operations with minimal supervision.
Learn more about real-world integration in this guide to jib crane installation.
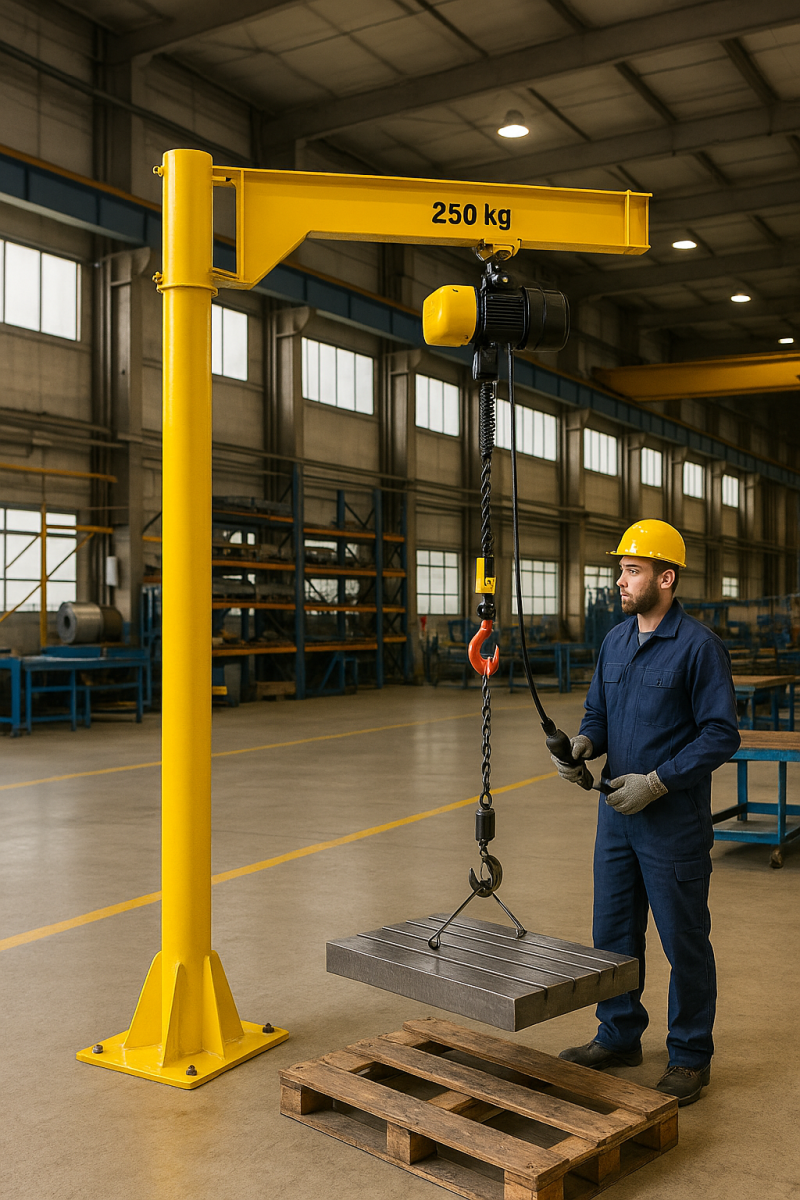

Smart jib cranes often support remote operation via:
Handheld controllers
Mobile apps
Touch-screen HMI panels
Technicians can operate or diagnose the crane remotely, minimizing the need for manual interaction. This is particularly useful in hazardous environments or for overhead installations like ceiling-mounted systems.
Modern smart jib cranes can connect to cloud platforms or local networks, enabling data capture and usage tracking. With IoT integration, managers can:
Monitor crane usage trends
Schedule maintenance proactively
Analyze error reports for efficiency improvements
This shift aligns with smart factory goals and improves long-term ROI.
To see how these features vary across crane types, read How Smart Features Vary by Jib Crane Type.

| Jib Crane Type | Automation Compatibility | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Freestanding | High | Heavy lifting with 360° rotation |
| Wall Mounted | Moderate to High | Space-constrained workflows |
| Ceiling Mounted | High | Multi-crane coordination above production lines |
| Articulating | Very High | Complex movement in tight areas |
| Pillar Mounted | Basic | Light lifting at workstations |
Each configuration has its own advantages depending on layout and load requirements. Explore a real-world setup here: jib crane application.
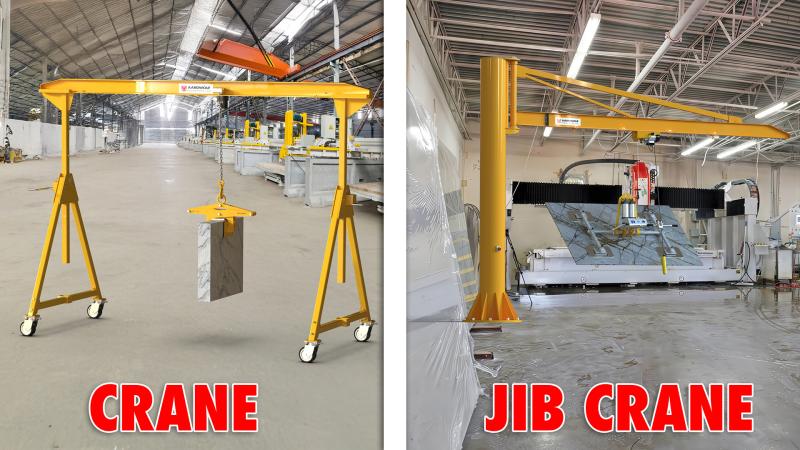

Wall-mounted systems are popular for applications where floor space is at a premium. To automate this configuration, you’ll need:
Motorized rotation unit
Smart hoist system with overload sensors
Control panel with programmable interface
Wall reinforcement for mechanical stability
Learn how to configure these systems with how to apply a jib crane wall-mounted in industry.
Before installing an automated jib crane, consider the following:
Cost: Upfront costs are higher but yield long-term savings.
Training: Staff must be trained to operate smart systems.
Integration: Compatibility with existing WMS or ERP systems must be verified.
Maintenance: Automated systems require regular software and hardware checks.

Automation is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity for companies aiming to improve safety, efficiency, and competitiveness. By enhancing traditional lifting systems with smart technologies, Jib Cranes are better positioned to serve a broader range of industrial applications.
From precision lifting in manufacturing to space-saving solutions in warehouses, each crane type—freestanding, wall mounted, ceiling mounted, or articulating—offers a path to intelligent automation. The key is choosing the right configuration for your specific needs and ensuring the crane is correctly installed and integrated.
Ready to make your lifting smarter? Begin with how to install jib cranes and progress through full automation with confidence.
References
1. How to operate a Jib Cranes safely
3. Over brace jib crane wall mounted
5. Is a Jib Crane a Gantry Crane
6. Articulated Jib Crane Wall Mounted
8. Manual Counterbalance Crane
10. Over Braced Jib Crane Column Mounted
Sign up to receive the latest info on new Aardwolf products, special offers and more.
By signing up you agree to receive emails from Aardwolf with news, special offers, promotions and other information. You can unsubscribe at any time.