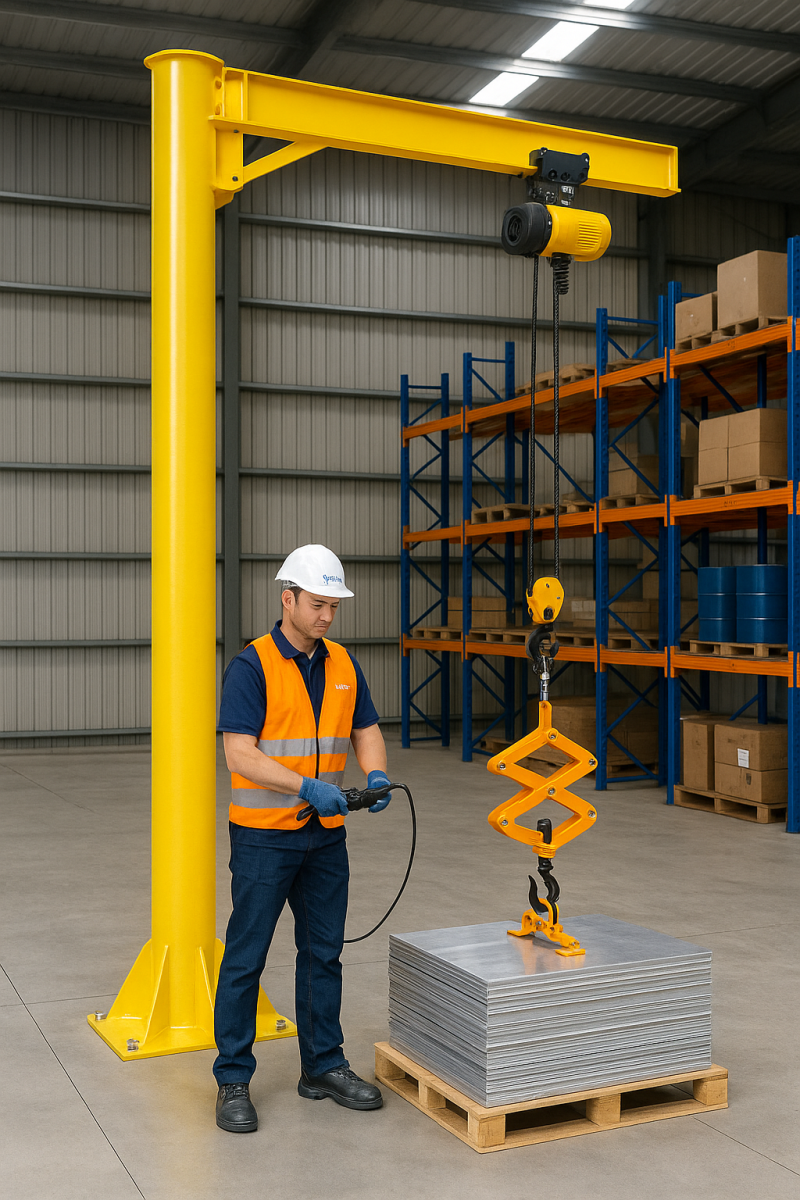




To choose, install, or maintain them effectively, you must understand their core structural components—from the boom and mast to the base and hoisting mechanisms. Whether it's a freestanding jib crane, a wall mounted jib crane, or an articulating jib crane, each model has unique structural demands.
If you’re unsure about the fundamentals, first explore what is a jib on a crane.
Failing to understand the structural composition of your jib crane can lead to:
Incorrect load distribution
Premature wear on bearings or anchor points
Safety violations
Excessive boom deflection
Knowing the specific use of structural components also helps you identify what crane best fits your operational needs. Learn more about what is a jib on a crane used for.

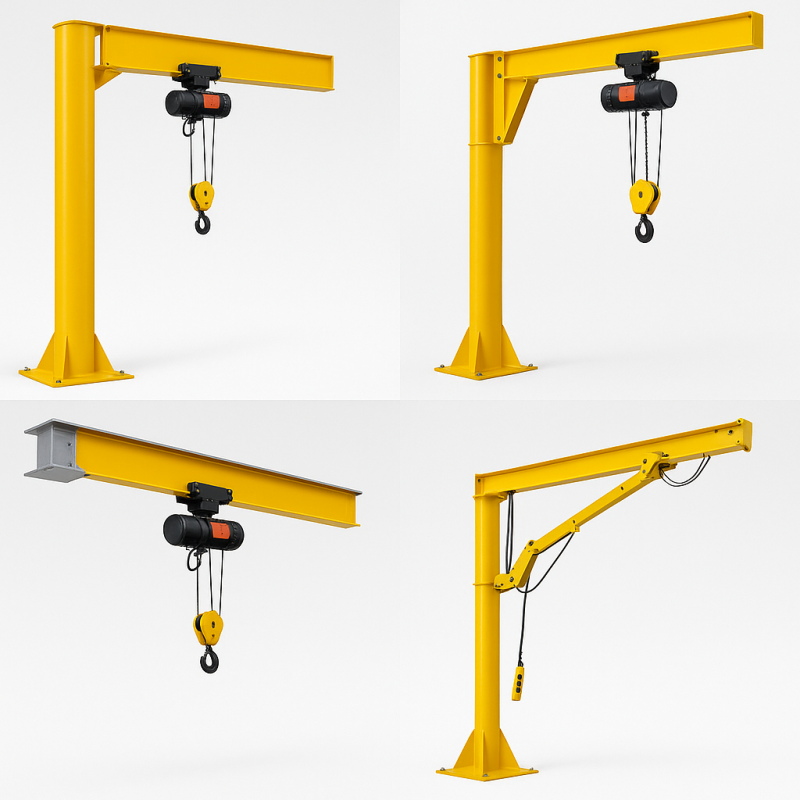
Purpose: The horizontal beam supporting the trolley and hoist.
Structure: Usually an I-beam or enclosed track made from high-tensile steel.
Variations:
Straight booms in freestanding and wall-mounted cranes
Dual-jointed booms in articulating jib cranes for flexible reach
Key concern: Excessive deflection under load
Purpose: Vertical support holding the boom.
Used in:
Freestanding jib cranes with floor-mounted columns
Pillar jib cranes for workstation use
Wall and ceiling-mounted cranes may connect directly to structural elements without needing a mast.
Purpose: Transfers crane loads to the floor or structure.
Types:
Concrete baseplate for freestanding cranes
Anchor bolts or wall brackets for wall-mounted cranes
Ceiling mounting kits for overhead integration
Important for: Leveling and long-term stability
Hoist: Performs the vertical lifting and can be electric, pneumatic, or manual.
Trolley: Moves horizontally along the boom; available in push-type or motorized versions.
Bearing Assembly: Located at the mast-boom junction for smooth movement.
Rotation Range:
Wall-mounted: 180° to 200°
Freestanding: Full 360° rotation
Maintenance Tip: Lubricate regularly for efficient operation.
For more: how to operate a jib crane
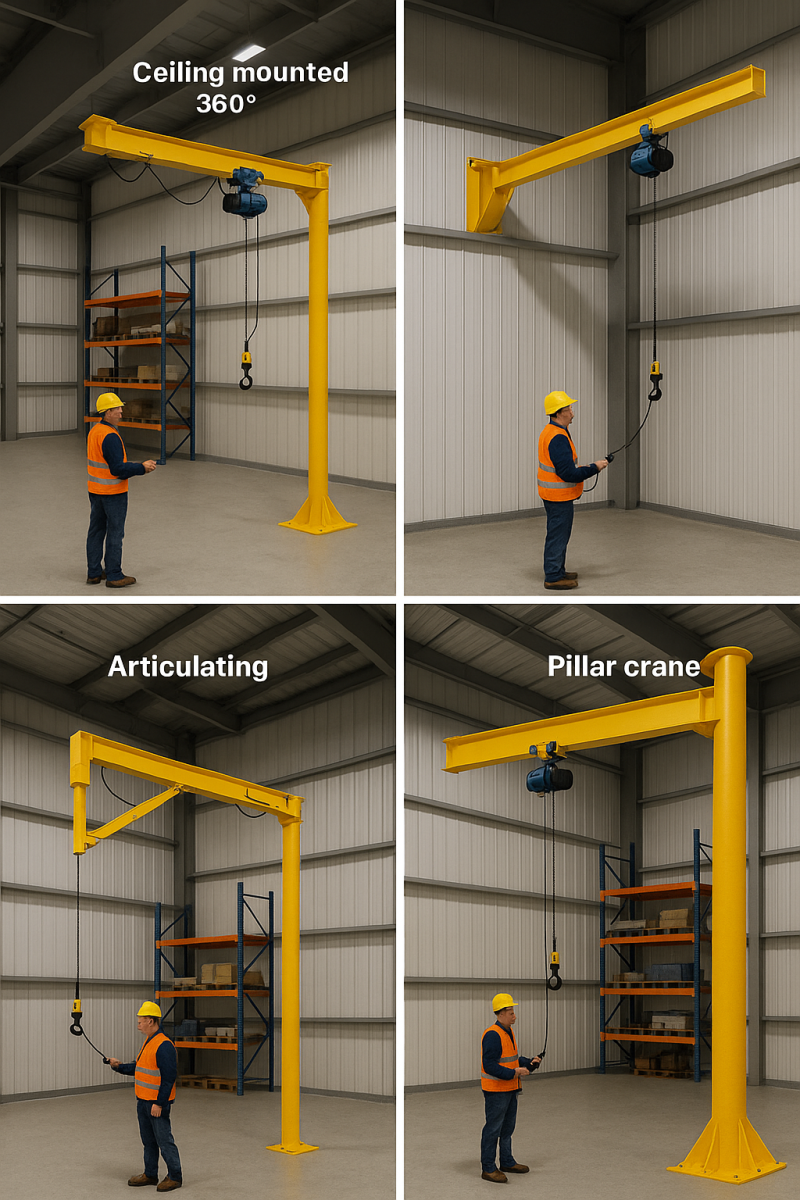
Includes a mast and baseplate
Supports full 360° rotation
Ideal for heavy loads in open-floor environments
Bolts to load-bearing columns or building walls
No mast required
Ideal for tight interiors or facility retrofits
Suspended from structural beams
Maximizes floor space
Used in cleanrooms or assembly lines
Dual-arm pivoted boom design
Ideal for complex work zones with machinery obstructions
Requires precise bearing and arm alignment
Shorter mast mounted to shop floors or portable bases
Serves light-duty workstation applications
Often modular for flexibility
Mild Steel (A36): Standard for general-use cranes
High-Strength Steel (A572): Used in higher-load, longer-reach models
Surface Treatments: Galvanization or powder coating for corrosion protection

| Feature | Jib Cranes | Overhead Cranes |
|---|---|---|
| Mounting | Floor, wall, or ceiling | Roof-runway or suspended girders |
| Flexibility | High (esp. articulating types) | Limited to runway track |
| Load Range | Light to moderate | Moderate to very heavy |
| Installation Ease | Easier, localized | Requires structural infrastructure |
Explore this in Jib cranes vs overhead cranes solutions.
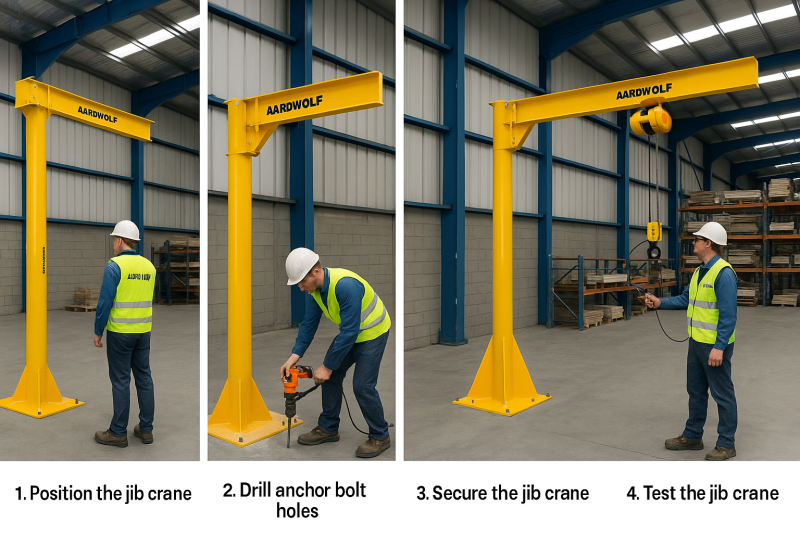
Use a spirit level or laser to align vertical mast
Cure anchor bolts fully before torqueing
Square mast with boom before operation
Learn exact steps from how to level a jib crane
Daily: Check for visible damage or misalignment
Monthly: Lubricate moving parts, tighten bolts
Quarterly: Test load under full arm reach to check deflection
Annually: Structural inspection by qualified personnel

The efficiency, safety, and longevity of jib cranes depend on proper structural design and maintenance. Whether you're working with a freestanding, wall mounted, articulating, or pillar jib crane, knowing how each component works will help you make better operational and purchasing decisions.
Looking to install or customize your crane? Explore how to build a jib crane for a real-world example and specifications.
References
1. How to operate a Jib Cranes safely
3. Over brace jib crane wall mounted
5. Is a Jib Crane a Gantry Crane
6. Articulated Jib Crane Wall Mounted
8. Manual Counterbalance Crane
10. Over Braced Jib Crane Column Mounted
Sign up to receive the latest info on new Aardwolf products, special offers and more.
By signing up you agree to receive emails from Aardwolf with news, special offers, promotions and other information. You can unsubscribe at any time.