How to Maximize Material Handling Equipment Systems for Manufacturing Productivity ?
Efficient material handling lies at the heart of modern manufacturing, bridging gaps between production steps, reducing waste, and ensuring on-time delivery.
By strategically selecting and integrating the right material handling equipment—from cranes and lifters to conveyors and securing devices—manufacturers can unlock significant gains in throughput, quality, and worker safety. This guide delves into proven strategies, core components, and best practices to help you design, deploy, and optimize complete material-handling systems for peak productivity.
Understanding Material Handling and Its Impact on Manufacturing
Material handling encompasses the movement, protection, storage, and control of raw materials, work-in-process items, and finished goods. In manufacturing environments, well-engineered handling material workflows:
-
Accelerate cycle times by minimizing unnecessary travel and bottlenecks
-
Reduce damage through secure handling and protection equipment
-
Optimize space utilization with efficient layouts and storage systems
-
Enhance worker safety by integrating ergonomic lifting equipment and automation
-
Lower overall costs via reduced labor requirements and maintenance needs
Industry leaders invest heavily in end-to-end handling material strategies, recognizing that an optimized system underpins reliable, scalable production.
Key Components of Material Handling Equipment Systems
Building a robust material-handling framework requires a harmonious blend of devices tailored to your unique workflows. Core categories include lifting equipment, automated transport solutions, storage/protection solutions, and load-securing devices.
Lifting Equipment Solutions
Modern lifting equipment ensures heavy or awkward loads are moved safely, precisely, and with minimal physical strain:
-
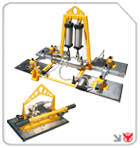
For versatile zone coverage, the right portable gantry crane offers adjustable spans and hoist capacities.
-
In-cell tasks benefit from the efficient wall-mounted jib crane, delivering 180°–360° swivel without consuming valuable floor space.
-
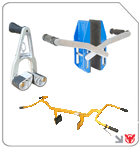
When handling stone or glass panels, a horizontal scissor lifter equipments grips slabs without marring surfaces.
-
High-throughput lines see gains from the slab lifter innovation, combining vacuum suction with powered rollers.
-
Fragile sheets are managed safely by the electric vacuum lifter AVLP4-1000, freeing operators from manual lifting
Together, these devices—from lifting clamp variants to vacuum lifter, slab lifter systems—form the backbone of any high-performance material-handling lineup.
Conveyor & Automated Handling Systems
Automation accelerates repetitive transport tasks while ensuring consistent flow:
-
Conveyor networks shuttle pallets, totes, and bulk materials between workstations.
-
Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS) intelligently retrieve items, cutting picking times.
-
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) follow optimized paths to deliver components on demand.
-
Sortation equipment routes products by SKU or destination, reducing manual sorting errors.
Implementing automated handling not only boosts throughput but also frees labor for higher-value activities
Storage & Protection Solutions
Proper storage prolongs asset life and preserves product integrity:
-
Racking systems, shelving, and vertical lift modules maximize density in limited footprints.
-
Industrial totes, bins, and pallets standardize unit loads for faster handling and stacking.
-
Protective packaging (e.g., cushioning inserts) guards against impact during transit.
An integrated approach to storage and protection ensures while materials remain secure, retrieval times stay low
Securing Solutions: Ratchet Tie Down Traps
Load stability is non-negotiable for safety and quality:
-
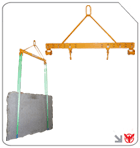
Ratchet tie down traps, such as the best durable straps ratchet tie down, employ high-tensile webbing and corrosion-resistant hardware.
-
These devices immobilize pallets, crates, and oddly-shaped loads during intra-facility transport or short-term staging.
-
Proper tie-down practices prevent load shift, reducing incidents and damage
Applying Core Principles to Optimize Your System
The Core Principles serve as guiding pillars for system design and continuous improvement:
-
Standardization: Uniform equipment and methods create repeatability.
-
Ergonomics: Equipment and tasks must align with human capabilities to reduce fatigue.
-
Space Utilization: Intelligent layouts maximize storage while maintaining flow.
-
Automation: Automate high-volume and repetitive tasks to boost output.
-
Inventory Management: Balance stock levels to minimize holding costs and shortages.
-
Equipment Selection: Match devices—like scissor lifter platforms or gantry cranes—to specific loads.
-
Unit Load Optimization: Combine individual items into standardized pallets or containers.
-
Environment: Ensure safety controls, lighting, and ventilation.
-
Cost Control: Evaluate total lifecycle cost, not just purchase price.
-
Work Positioning: Situate workstations, storage, and equipment for shortest, safest workflows. Embedding these principles drives leaner, safer, and more flexible operations.
Process Flow Optimization for Maximum Throughput
Beyond individual devices, the sequencing and layout of material flows critically affect productivity. Follow these steps:
-
Process Mapping: Visually chart every handling step—receiving, storage, picking, packing, shipping—to expose inefficiencies.
-
Zone Design: Group related tasks (e.g., kitting, assembly) to reduce travel distance and simplify oversight.
-
Cross-Docking: Bypass storage by transferring inbound goods directly to outbound areas when product profiles allow.
-
Lean Techniques: Apply 5S and Kaizen to maintain cleanliness, order, and continuous incremental improvements.
A well-tuned flow ensures raw materials arrive just-in-time and finished goods depart on schedule
Standardization and Unit Load Optimization
Standard unit loads—such as pallet dimensions and container types—enable rapid transfers via forklifts, conveyors, and automated systems. By consolidating varied SKUs into common load profiles, you minimize handling complexity and equipment changeovers.
Ergonomics and Safety Integration
Integrate ergonomic devices—like scissor lifter tables and vacuum lifters—to eliminate manual bending and heavy lifting. Coupled with training and SOPs on the importance of material-handling equipment, these measures significantly lower injury rates and absenteeism.
Space Utilization and Layout Efficiency
Maximize vertical storage with high-rise racking or vertical lift modules. Use narrow-aisle forklifts and overhead systems to shrink aisle widths without hindering accessibility. Effective layout planning balances density with flow.
Partnering with Material Handling Companies for Long-Term Success
In a dynamic manufacturing landscape, selecting supportive material handling companies ensures sustained performance:
-
Customized Solutions: Look for vendors offering tailored system design, from lightweight manual aids to advanced automated lines.
-
End-to-End Services: Prioritize partners who provide consultation, installation, operator training, and preventative maintenance.
-
Prime Equipment Brands: Align with reputable manufacturers whose lifting equipment—gantry cranes, lifters, conveyors—has proven reliability.
A strong partnership delivers ongoing optimization, rapid issue resolution, and upgrades that keep your system competitive.
Conclusion
Maximizing manufacturing productivity hinges on a holistic approach to material handling equipment systems. By combining specialized lifting tools—such as lifting clamp devices, vacuum lifter slab lifter units, and scissor lifter platforms—with robust conveyors, racking, and securing solutions like ratchet tie down traps, you can create fluid, high-capacity workflows. A material-handling infrastructure that accelerates throughput, slashes costs, and protects your most valuable asset—your workforce.
Invest today in an optimized material-handling ecosystem to build the resilient, agile manufacturing line of tomorrow.












































Follow us on: