How Can You Optimize Your Material Handling Processes for Maximum Efficiency?
Material handling refers to the short-distance movement, storage, control, and protection of materials and products throughout the manufacturing, warehousing, distribution, consumption, and disposal processes
Understanding Material Handling and Its Importance
What Is Material Handling?
It includes activities such as loading and unloading trucks, placing individual items on pallets, and retrieving products from shelves for shipment. A robust material handling strategy ensures that each item is moved safely and efficiently within or between facilities, reducing delays and minimizing waste
Examples of types of material-handling include manual handling, mechanical handling, storage operations, and fully automated systems, each tailored to the specific needs of the material handling industry.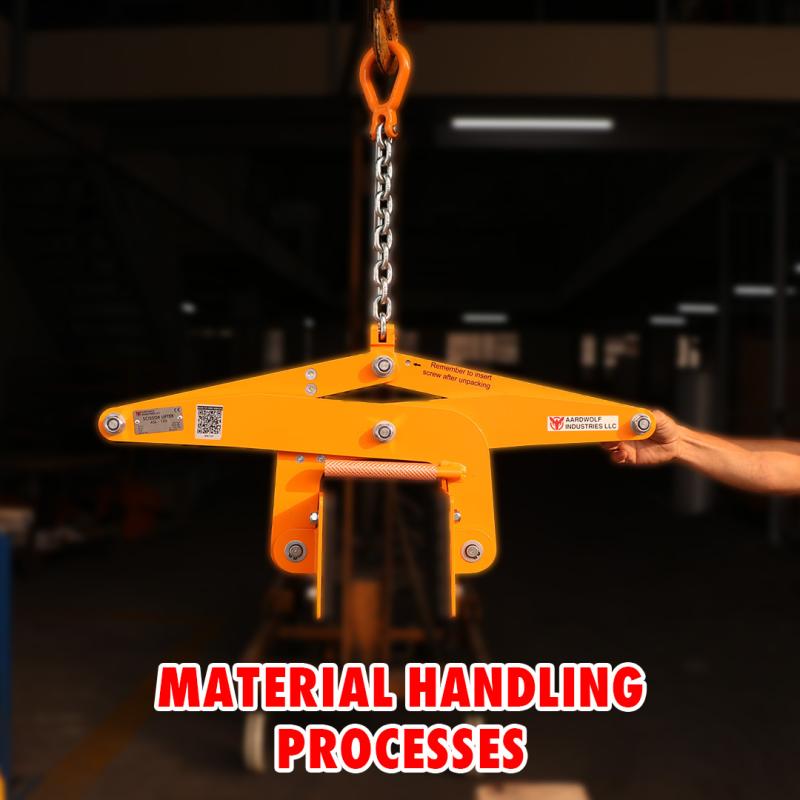
Why Material Handling Matters in the Supply Chain
A well-designed material handling system directly impacts operational performance. By optimizing handling material workflows, companies can:
-
Improve customer service through faster order fulfillment
-
Lower operational costs by reducing unnecessary movement
-
Enhance worker safety and reduce accident rates
-
Minimize product damage during transit and storage
These gains are critical in today’s competitive landscape, where material handling companies and supply-chain partners must deliver speed, accuracy, and safety.
The Ten Principles of Material Handling
-
Planning: Systematic design of all material handling operations.
-
Standardization: Consistent methods and equipment without sacrificing flexibility.
-
Work: Simplification of tasks to eliminate unnecessary movement.
-
Ergonomics: Alignment of tasks to human capabilities to protect operators.
-
Unit Load: Consolidation of individual items into larger, more manageable loads.
-
Use of Space: Maximizing vertical and horizontal storage areas.
-
System: Integration of individual activities into a cohesive operational flow.
-
Automation: Adoption of mechanized and automated solutions where feasible.
-
Environment: Design consideration for energy efficiency and environmental impact.
-
Life Cycle Cost: Economic analysis that accounts for total cost
Core Components of Material Handling Equipment
Transportation Equipment
Efficient movement of goods relies on the right fleet of transportation assets:
-
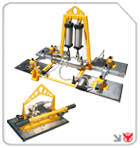
Cranes (including gantry crane material handling and bridge cranes) handle heavy and bulky items. For example, consider overhead gantry crane equipment when selecting a high-capacity lifting solution.
-
Forklifts and pallet jacks transfer unit loads on wood pallets.
-
Conveyors move products along production lines, reducing manual handling.
These systems form the backbone of material-handling equipment and are critical for streamlining workflows.
Storage and Protection Equipment
Proper storage preserves product integrity and optimizes space:
-
Pallet racks and shelving systems use vertical space efficiently.
-
Industrial packaging and cushioning protect fragile or sensitive items.
-
Custom crating solutions guard against damage during long-distance transport.
Together, storage and protection solutions ensure goods remain intact and accessible when needed.
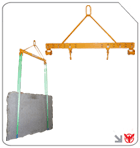
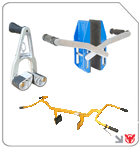
Specialized Lifting and Securing Solutions
For handling irregular or heavy loads, specialized lifting equipment is indispensable:
-
Lifting clamp devices offer a secure grip on beams, plates, and profiles.
-
Scissor clamp lifter equipments provides one-person operation for precise handling of sheet materials.
-
Vacuum lifter slab lifter systems such as the vacuum glass lifter Pro AVLP4 enable safe, non-marking lifting of glass or stone.
-
Slab lifting with roller AL50AR combines vacuum suction and roller support for seamless movement of heavy panels.
-
Ratchet tie down traps secure loads during transit and storage.
Strategies to Optimize Material Handling Processes
Streamlining Workflow and Facility Layout
-
Process Mapping: Chart every handling step to identify redundancies.
-
Zone Design: Group similar operations (receiving, picking, packing) to minimize travel distance.
-
Cross-Docking: Transfer goods directly from inbound to outbound docks when possible, bypassing storage.
Implementing Ergonomic Lifting Equipment
Investing in ergonomic lifting solutions reduces strain injuries and boosts productivity:
-
Deploy scissor lifter platforms for adjustable lifting heights.
-
Use lifting clamp tools to handle odd-shaped loads safely.
-
Integrate vacuum lifters to eliminate manual bending and lifting.
Leveraging Automation and Technology
Automation can transform throughput and accuracy:
-
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) handle repetitive transfer tasks.
-
Conveyor systems integrated with sensors optimize flow.
-
Smart packaging stations adapt to product dimensions.
-
Vision-guided robotics pick and place delicate items.
-
Integrate IoT sensors on gantry cranes and forklifts to track asset utilization in real time.
Choosing the Right Crane Solutions
Selecting crane systems tailored to your workload enhances handling material efficiency:
-
For ceiling-mounted loads, consider wall mounted jib crane equipment.
-
For larger spans and heavier loads, overhead gantry crane equipment offers superior capacity and coverage.
Best Practices for Material Handling Safety
Training and Standards
-
Establish clear SOPs aligned with industry regulations.
-
Conduct regular operator training on lifting equipment and safety protocols.
-
Partner with certified material handling companies to stay current on best practices.
Maintenance and Inspection
-
Schedule preventive maintenance for material-handling equipment.
-
Perform daily safety checks on cranes, hoists, and vacuum lifters.
-
Track metrics such as mean time between failures (MTBF) to optimize lifecycle cost.
Selecting the Right Material Handling Partner
When evaluating vendors, consider:
-
Industry expertise in your sector (e.g., automotive, aerospace, electronics).
-
Range of material handling equipment offerings, from conveyors to vacuum lifters.
-
Ability to provide turnkey solutions, from design and installation to ongoing support.
-
Strong track record among material handling companies and positive client testimonials.
Conclusion
Optimizing material handling processes is a multifaceted endeavor that combines strategic planning, the right mix of equipment, ergonomic solutions, and advanced automation. By understanding the fundamental principles, investing in specialized lifting and securing devices, and leveraging modern technologies, businesses can achieve maximum efficiency, improve safety, and maintain a competitive edge in the material handling industry.












































Follow us on: